Learners from ages zero to eighteen have a lot to be excited about. In the last 365 days, 74 companies focused on the K12 demographic (both in and out of school) have been funded by venture backers for a total of $427 million[1]. At the Seed Fund, we participated in 13 of these and got to see many more. Here, we share with you our analysis of the types of companies funded by stage. In later posts, we’ll reconcile this data with educator-identified gaps in the edtech landscape. Our goal is to highlight areas of greatest need in order to catalyze entrepreneurial energy and interest from funders into these places. The edtech landscape is dynamic so please note we expect our analysis to be iterative and will evolve accordingly. We hope you find this useful and welcome any thoughts or comments you might have.
We’ve broken edtech ventures into two categories: tech that supports learning in schools and tech that supports learning outside of schools (funding was split about evenly between the two). This bifurcation reflects the current realities of the space: surprisingly few learning applications reach across home and school. We expect this line will blur as technology advances in both home and school. As others have noted, we expect education will follow the consumerization of enterprise trend, meaning the best products from the consumer space will find their way into schools and vice versa resulting in a more porous learning boundary between schools and home.
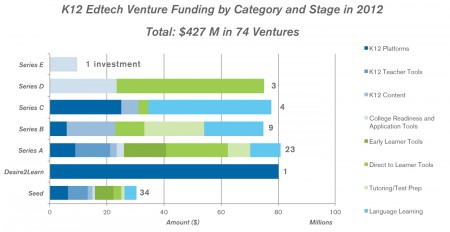
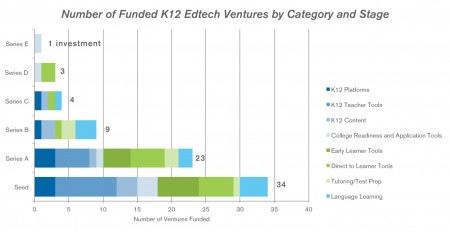
This is what the funding breakdown of the categories looks like, divided by stage. At the bottom we graph the quantity funded by stage and category also.
A couple of trends to call-out:
- Money continues to flow to large market opportunities such as college and test prep, tutoring, and language learning.
- India-focused venture activity in education is on the rise with investments in gaming, content, tutoring, and more. Please note companies exclusive to foreign markets are not included in the graphs or data.
- Funding for K12 is more concentrated in the early stages reflecting the influx of talented web and mobile entrepreneurs starting new companies and new, early-stage funding sources.
- Total funding is roughly evenly split between learning tools for schools and supplemental (direct to consumer) learning tools.
Technology for Schools and Teachers
K12 Platforms
- School-based platforms that enable the creation of products and/or applications supporting present or future development like Education Elements or edmodo. Platforms always have an API for developers.
K12 Teacher Tools
- School-based tools that aid a teacher in the classroom. Can be domain specific like Desmos (math) or more horizontal like Nearpod (presentations). Sometimes teacher tools grow into platforms (e.g. engrade started as a gradebook, but now has exposed an API that allows 3rd parties to integrate content).
K12 Content
- Content creation or curation sites for use in the classroom – the future thinking ones are all common core aligned like Learnzillion, and they often integrate with platforms for greater distribution
Technology for Supplemental Learning (outside of school learning)
Early learner tools
- Platforms, tools, content and app directories focused on early childhood learning. These are non-school based and often have direct to consumer revenue models. Kidaptive, Fingerprint and DuckDuckMoose are high-quality examples in this space.
Direct to Learner Tools
- Applications that include content, platforms and tools designed to be used directly by a more independent learner. Can be social learning networks or supplemental content like Codecademy or Stencyl. Gaming is a large subset of direct to learner tools, and includes companies that develop suites of educational games like Lumosity. We do not include casual games that lack an educational bent. Some refer to a segment of companies in this category as edutainment.
Tutoring/test prep
- An entire industry exists around preparation for high stakes testing, and logically is moving digital. Includes tutor matching sites like Tutor-group as well as content practice sites like Benchprep.
College Readiness and Application tools
- Includes infrastructure tools like Parchment that support the college admission process as well as Mytonomy, a tool offering near-peer college advice.
Language Learning
- Applications used in language learning – many are English language learning like Open English. This is a large, diverse, internationally-focused market.
Click to view full size:
*Okay, 352 from the time of writing.
Go here to see more data and please post questions and comments in the comments section below. Thank you to NewSchools Seed Fund Principal, Jen Carolan, for her contribution to this article.
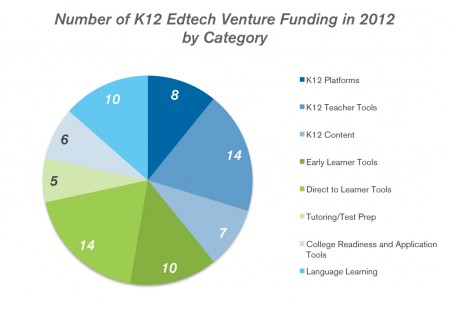
Update 1/4/13: Visualization of number and amount of investments by category.
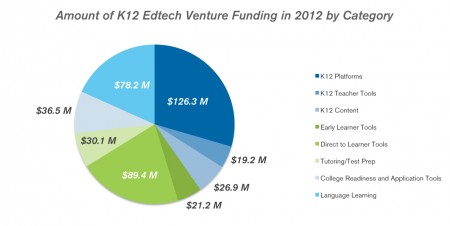
Update 1/7/13: “Amount of K12 Edtech Venture Funding in 2012 by Category” Graph: Figures abbreviated to millions.
Click to view full size:
Click to view full size: